

Opioids, anti-inflammatories, muscle relaxants topical pain medications may be prescribed. Managing pain is very important for a faster recovering. Recovery from a broken fibula may take six weeks or longer, while tibial shaft fracture may take 4 to 6 months to heal completely.
#Fracture fibula skin
With this method, the metal screws or pins project outside the skin and help to keep the bones in place. Usually, only most severe open fractures require external fixations. The fixations can be internal (under the skin) or external, (attached to a bar outside the skin). The bone fragments will first be repositioned (reduced) into their normal alignment then the surgeon will use plates, screws or rods to hold the broken portions of the bone together. In this procedure, called Open Reduction and Internal Fixation ORIF, the orthopedic surgeon will perform invasive surgery on the bones.
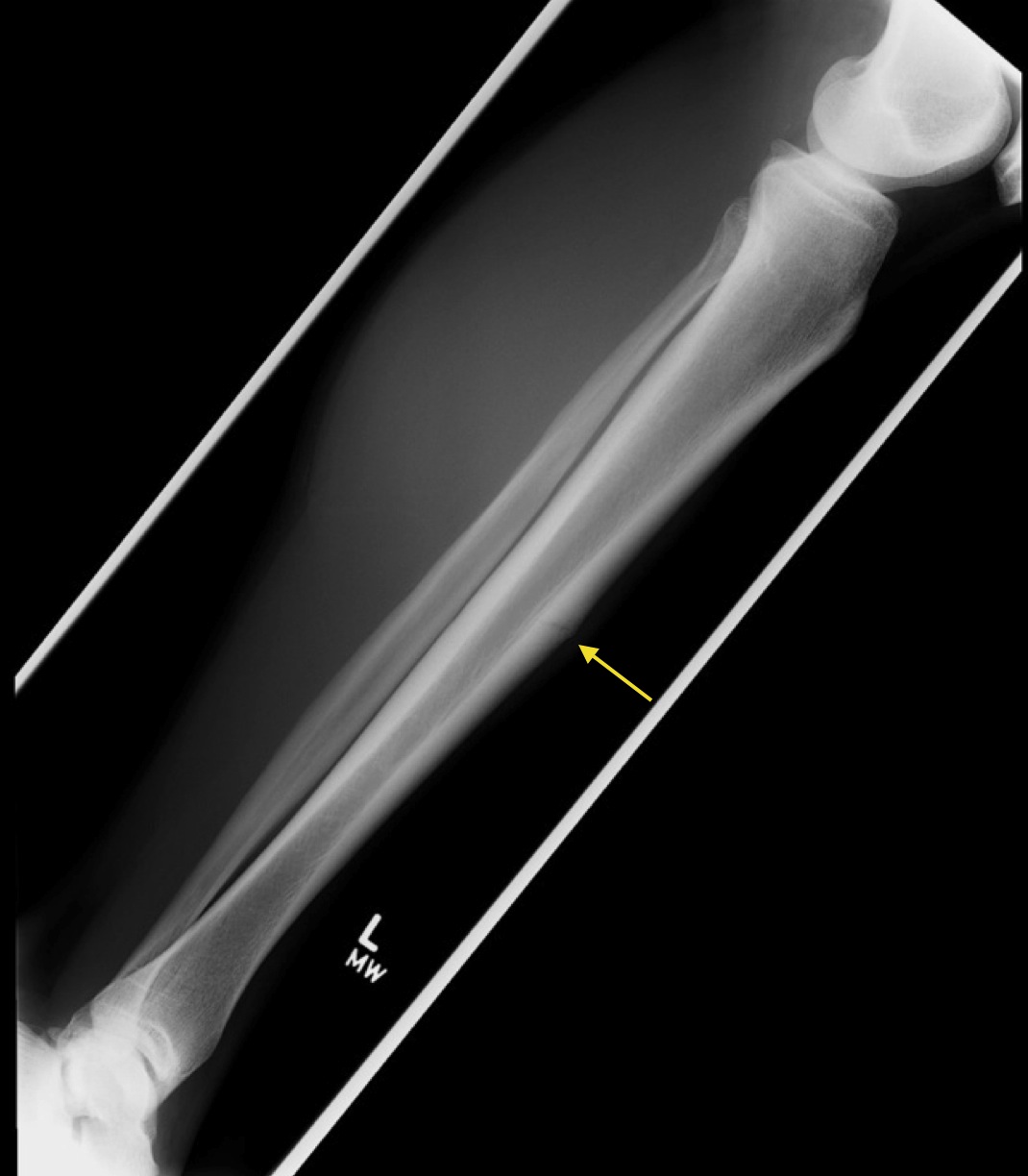
The orthopedic surgeon will align the bones in the correct position without surgery ( closed reduction). Treatment for a Tibial Shaft Fracture or Fibula fracture depends on the type of fracture and how severe it is.Ĭlosed or simple fractures may not need surgery. X-rays or CT scan may be ordered to have more precise imaging of the break. The orthopedic surgeon will perform a physical examination to look for signs and symptoms of a fracture and will ask for your medical history. stress fracture which is due to repetitive injury.avulsion fracture, when a small part of the bone gets pulled off.in the middle of the leg ( shaft fracture).around the ankle (lateral malleolus fracture).Ankle fracture: fracture of the ankle joint.Tibial plateau fracture: fracture of the tibia at the knee joint.Open fracture, when the bone punctures the skin.Displaced fracture, when bones are out of alignment.Stable fracture, when the pieces of bone still line up correctly.Tibia fractures vary depending on the force that caused the break. Bone poking over the skin at the fracture site.Difficulty or total inability to walk and bear weight on the leg.sport injuries (skiing, soccer, tennis, basketball and sports that imply much twisting or cutting).The tibia is the larger one and it is the most often fractured long bone in the body due to its superficial position in the leg.Ī tibial or a fibular shaft fracture usually happens when more pressure is put on the bone than it can handle or when excessive rotational stresses are applied.Ī broken leg is typically caused by a major force due to high-energy collision such as To arrange an assessment with a specialist physiotherapist call .uk on 03 or book online.The tibia and fibula are the two long bones of the leg that run parallel to each other. This may involve low impact ‘cross training’, swimming, deep water running and cycling. A programme will be developed to allow you to maintain your cardiovascular fitness and muscle strength without delaying healing. This may initially involve a period of rest, bracing and the use of crutches and icing to help with your pain. From this your physiotherapist can develop an appropriate treatment plan. This may require the referral for imaging techniques such as a MRI scan. Initially, your physiotherapist can provide you with a diagnosis. Physiotherapy is important in the treatment of a stress fracture of the fibula. Physiotherapy treatment for a stress fracture of the fibula. If this does not happen, you may be at risk of a complete bone fracture or further stress fractures when you recommence participation. This can potentially lead to a longer lay off from normal activity and, in some cases, a complete fracture of the fibula.Ĭould there be any long-term effects from a stress fracture of the fibula?Ī stress fracture of the fibula does not produce any long-term effects, if it is properly treated, and the cause identified and addressed. If you continue to exercise you could weaken the bone further and delay healing. If you suspect that you have a stress fracture of your fibula you should not continue to exercise. What shouldn’t I do if I have a stress fracture of the fibula? Above: Calf strengthening exercises conducted under supervision of specialist MSK physiotherapist


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
